Over the past decade, the availability of satellite data and maps through online repositories and geoportals has increased significantly. Leading data-generating organizations are now making their vast repositories openly accessible to the public. This shift has greatly enhanced the utilization of geospatial data in planning, governance, and decision-making processes. However, while the abundance of data presents numerous opportunities, it also creates challenges for users in selecting the most appropriate datasets for their specific needs.
Simultaneously, geospatial technology has emerged as an essential tool in various thematic applications, particularly in governance, development and policy making. However, for optimal utilization of this technology, specific skill sets are required at the user end. A significant number of users still hesitate to adopt geospatial tools due to their limited technical proficiency, hindering the full-scale deployment of these technologies in critical applications.
The recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have significantly improved the accessibility and usability of Internet-based data resources. AI-powered applications, particularly those leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP), are revolutionizing how users interact with complex datasets. NLP enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language, which is now being widely used in search engines, translation services, chatbots, sentiment analysis, and many more applications.
Several AI-powered models, such as ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Gemini, and MS Copilot, exemplify the power of NLP in making AI interactions more intuitive and effective. These models have transformed various domains, including content creation, coding assistance, and online tutoring, by providing human-like responses and understanding complex queries.
One of the groundbreaking applications of AI in geospatial technology is “Text-to-Map.” This concept refers to the ability to generate a map based on a natural language description. By integrating NLP and Generative AI, mapping applications can now interpret user queries in plain language and convert them into dynamic visual spatial representations.
An NLP-based interactive GeoChatBot has been developed at IIRS Dehradun to generate maps using simple text and voice commands. The system is trained using vector and raster spatial data specific to Uttarakhand State, leveraging a Large Language Model (LLM) to interpret user queries and convert them into geospatial operations. The software is further customized with Python-based geo-processing tools for raster data and PostGIS for handling vector data queries. When a user inputs a request in natural language, the LLM processes it and translates it into a spatial operation, which is then executed by a Python-based processing engine developed during the study. This enables seamless map generation and spatial analysis without requiring users to have technical expertise in GIS.
Users can describe locations, routes, or areas of interest conversationally, and the system will generate corresponding maps that can be refined in real time through further interactions. This advancement allows for a more seamless and intuitive mapping experience, effectively enabling users to “talk” to their maps and receive precise, customized outputs.
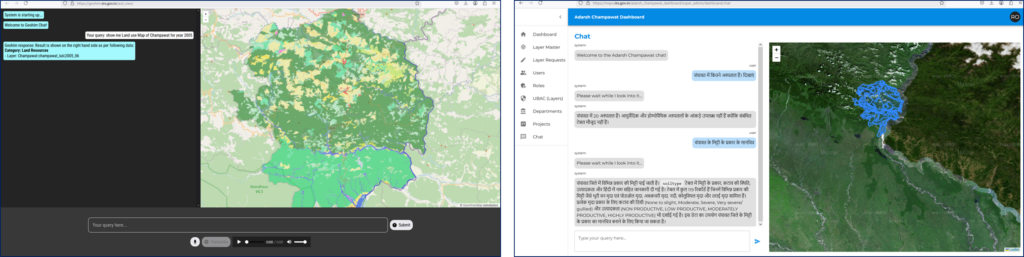
Figure 1– Interactions with Maps using simple language
The integration of AI-driven tools in geospatial technology addresses a critical challenge: the hesitation of non-technical users to engage with geospatial data. By simplifying access and interpretation, AI-powered solutions like Text-to-Map remove technical barriers, making advanced mapping capabilities accessible to a broader audience.
The developed system at IIRS has potential applications in urban planning, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and GIS-based decision support systems, making geospatial data more accessible and interactive.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in geospatial technology will only expand, fostering more user-friendly, efficient, and intelligent applications. The convergence of satellite data accessibility, AI advancements, and NLP-driven mapping solutions is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with geospatial information. By embracing these innovations, decision-makers and the general public alike can leverage the full potential of geospatial technology for informed planning and sustainable development.