El Niño is a buzzword in year 2024 which is a climatic phenomenon characterized by the periodic warming of the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, leading to substantial global changes observed in weather patterns. Due to El Niño effect in year 2024, the scorching heat is observed in various parts of the world specially in India the large section of population is severely affected. The term “El Niño,” meaning “The Little Boy” in Spanish, was coined by Peruvian fishermen who observed the warmer ocean waters during the month of December. Under normal conditions, trade winds blow from east to west along the equator, pushing warm surface waters toward Asia and allowing cooler water to rise near the South American coast. The El Niño effect is typically Occurring every two to seven years and lasting several months, El Niño arises when trade winds weaken or reverse, causing warm water to build up in the central and eastern Pacific. This disruption affects typical oceanic and atmospheric circulation result severe changes in weather patterns.
The effects of El Niño in India are profound, influencing various aspects of the country’s climate, agriculture, and economy. El Niño is often associated with higher-than-average temperatures, leading to severe heatwaves across India. These heatwaves can have serious health impacts, causing heat-related illnesses and fatalities. The overall increase in temperature variability can affect both human health and the environment. In this summer of 2024, we are observing highest temperature ever recorded in the history of human being in various part of the country. However, the year 2024 is not the first El Niño year for India rather it’s a regular climatic phenomenon but its severity is an alarming condition. The onset of the monsoon season can be delayed during El Niño years, further disrupting the agricultural calendar and water resource management. Variations in precipitation and temperature can impact crop yields, potentially leading to food shortages and economic difficulties due to decreased agricultural productivity. Warmer ocean temperatures can disrupt marine ecosystems, causing fish to migrate to cooler waters and affecting fisheries and the livelihoods that depend on them. Changes in weather patterns can lead to natural disasters such as cyclones, floods, and wildfires, resulting in significant human and economic losses. El Niño is a natural phenomenon and humans cannot control or prevent it but its effects can be mitigated through improved early warning systems and preparedness strategies. Advances in climate science have improved the prediction of El Niño events, allowing for proactive measures like water resource management and disaster preparedness to reduce potential damage.
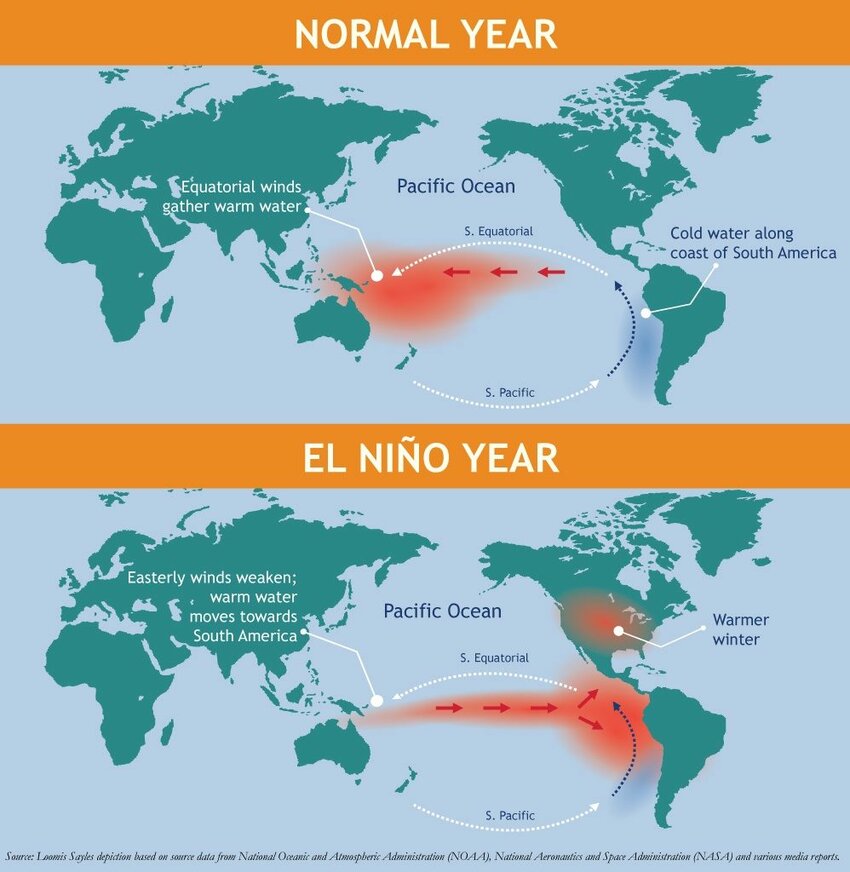
Illustration of the physical process of El Niño. Courtesy of concern worldwide US.
Plantation efforts, including reforestation and afforestation, can play a crucial role in mitigating some of the impacts of El Niño. By reducing the overall greenhouse gas concentrations, plantation can help stabilize global weather patterns, potentially lessening the intensity of El Niño events over the long term. The tree cover can help moderate local temperatures, reducing the likelihood of extreme temperature events such as heatwaves, which are often exacerbated during El Niño years. Trees facilitate the infiltration of rainwater into the soil, replenishing groundwater supplies. This can be crucial during periods of drought, providing a more stable water supply. Tree roots stabilize the soil, reducing erosion and preventing land degradation. This is particularly important during heavy rains, which can be more intense during certain phases of El Niño. To maximize the benefits of plantation efforts in mitigating El Niño effects, it is important to focus on the strategies such as choosing the right tree species that are native and adapted to local conditions ensures better survival rates and ecological benefits, engaging local communities in plantation projects ensures long-term maintenance and success of reforestation efforts and combining reforestation with sustainable agricultural practices, water management, and conservation strategies creates a holistic approach to climate resilience.



